Over the past three decades, red dot sights evolved from curiosities into essential firearms accessories enhancing the speed and accuracy of tacticians, law enforcement, military personnel, and recreational shooters alike. But what exactly are these devices, and how does projecting a red dot onto a lens improve marksmanship fundamentals?
This article peeks inside the technology powering modern red dot sights, outlining key components and operating concepts that altered modern shooting techniques. Understanding the science behind this equipment provides insight into matching the optimal configuration to your firearms and usage cases.
(Reading Time: 4-6 Minutes)
Red Dot Sight Components
While diverse implementations exist across manufacturers, red dot sights share common core components that enable their novel aiming functionality. These include:
Housing and Body – Encloses internal optics and electronics, typically constructed from aluminum or titanium for lightness and durability. Waterproofing prevents fogging.
LED Emitter – Light emitting diode projects illumination, either as a pinpoint or reticle pattern. Wavelength determines red or green color.
Reflective Coating – Concave mirror surface reflects and focuses LED into collimated dot. Maximizes dot intensity throughout lens.
Optics – Front and rear anti-reflective coated lenses provide clear viewing and protect emitter.
Power Source – Battery powers LED and electronics, typically CR2032 or AAA cells for compactness.
These elements integrate to supersede iron sights for fast target engagement at close and medium ranges. Durability also suits defensive roles. Next we will overview the operating principles guiding dot production.
Operating Principles
An LED housed in the sight body powered by the onboard battery emits a pinpoint beam of light either as standalone point or traced into a circle, crosshair or dot pattern. This gets focused by the concave reflective coating onto the rear lens as a collimated dot.
Because this dot is projected forward onto the lens plane rather than etched onto the lens itself, the illuminated dot stays optically aligned relative to the target regardless of viewer position. This differs from iron sights requiring precise eye alignment for accuracy.
The illuminated dot simply floats the sight, enabling target focus and engagement with both eyes open using unlimited eye relief. Adjustments alter dot intensity and polarity to match ambient lighting conditions and user vision. Next we will overview common red dot sight designs and mounting options.
Types of Red Dot Sights
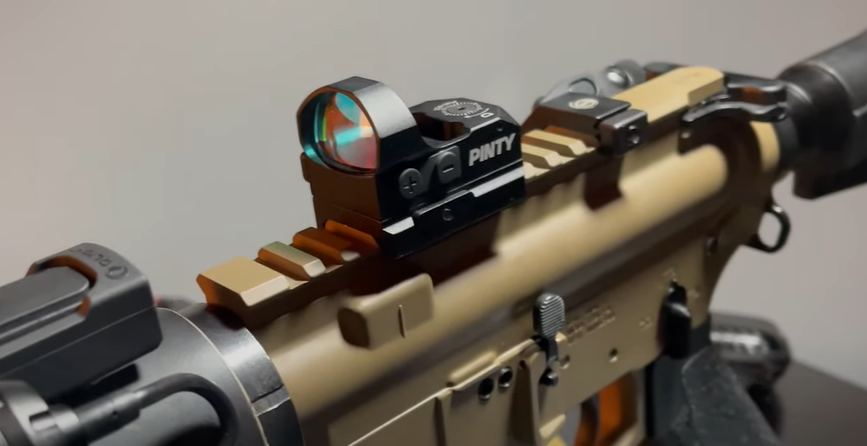

Micro Red Dot Sights Micro red dot sights are compact, lightweight versions of their full-sized counterparts, designed primarily for pistols but also used on rifles. Their small size makes them ideal for shooters who prefer a minimalistic setup without sacrificing functionality. Micro red dots typically mount easily on a variety of platforms and are perfect for concealed carry purposes. Despite their small size, they offer quick target acquisition and can be as rugged and reliable as larger models, making them a versatile choice for both casual and professional use.
Reflex Sights Reflex sights, a type of tubeless red dot sight, utilize a reflective glass lens and an LED to project the reticle. They are renowned for their simplicity and fast target acquisition. Reflex sights are incredibly lightweight and compact, offering a wide field of view. They are versatile for different lighting conditions, with reticles that can auto-adjust in brightness or can be manually set. Ideal for close to medium-range shooting, reflex sights are commonly used in tactical scenarios, competitive shooting, and by law enforcement.
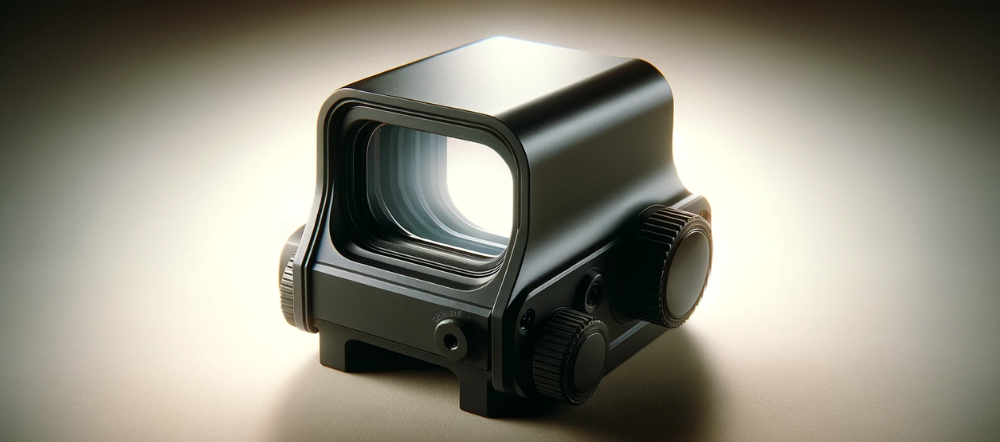

Holographic Sights Holographic sights are advanced optics that use laser technology to project a holographic reticle onto the viewing window. These sights offer a unique advantage in that the holographic reticle remains in focus at various distances, allowing for more precise aiming. They provide a wide field of view and are excellent for rapid target engagement, especially in dynamic situations. Holographic sights are typically more durable and offer better visibility in bright light conditions compared to traditional red dot sights. They are widely used in military, law enforcement, and competitive shooting sports.
Each type of red dot sight offers distinct advantages, catering to the diverse needs and preferences of shooters in various scenarios. From the robust full-sized models to the technologically advanced holographic sights, the choice depends on factors like firearm type, intended use, and personal preference.
Advantages of Red Dot Sights
Speed – Red dots allow faster sight alignment and engagement than iron sights, especially in competitions and defensive applications.
Accuracy – Precise dot placements enable enhanced accuracy across most shooting distances.
Unlimited Eye Relief – Consistent dot visibility from any eye position behind sight unlike iron sights.
Depth Perception – Both eyes open ability enhances situational awareness and depth judgement.
Reliability – No intricate moving parts and resistant sealing delivers consistent performance.
Low Magnification – Unlike scopes, avoids narrowly magnifying jitters that displace aim.
Red dot advantages make them ideal for tactical and home defense weapons where fast target transitions matter most.
Considerations When Using Red Dots
Limited Range – Maximum accuracy limited to 100-200 yards depending on dot size. Scopes better beyond.
Backup Iron Sights – Many users add folding iron sights if electronics fail.
Battery Life – Turning dot off when not in use preserves thousands of hours of battery life.
Matching Gun Use – Smaller pistol dots differ from larger rifle sights. Match accordingly.
While offering advantages over irons in many regards, shooters must align red dot strengths to their needs and maintain properly as electro-optical tools.
Conclusion
Red dot sights provide enhanced speed, target acquisition, depth perception, and accuracy at short to medium ranges through an ingeniously simple concept - projecting an illuminated reference point geared for intuitive sight alignment.
Understanding the electro-optical components powering this versatile technology provides insight into configuring the optimal red dot sight for your specific firearms and shooting needs. With proper application, red dots prove a valuable augmentation to skillsets across defensive, sporting, and tactical disciplines.